No edit summary Tag: 2017 source edit |
Robert Vogel (talk | contribs) Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|boxtype=important | |boxtype=important | ||
|header=Migration from 4.4 | |header=Migration from 4.4 | ||
|text=With BlueSpice 4.5 there were important changes to the container portfolio: | |text=With BlueSpice 4.5 there were some important changes to the container portfolio: | ||
# There are no "all-in-one" containers anymore. Neither for FREE, | # There are no "all-in-one" containers anymore. Neither for FREE, nor for PRO and FARM editions | ||
# The "distributed-services" setup for PRO and FARM edition has been reworked | # The "distributed-services" setup for PRO and FARM edition has completely been reworked | ||
If you are upgrading from one of the above-mentioned setups, please refer to the [[{{FULLPAGENAME}}/Migration_4.4 to 4.5|migration guide]] | If you are upgrading from one of the above-mentioned setups, please refer to the [[{{FULLPAGENAME}}/Migration_4.4 to 4.5|migration guide]] | ||
|icon=yes | |icon=yes | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
=== | ===Overview=== | ||
Since version 4.5, BlueSpice MediaWiki can be easily installed using a stack of Docker container images. Everything is build in a modular way to allow different types of setups. | |||
The most common cases are | |||
# "All-in-one" (with and without Let's Encrypt) | |||
# Custom database and search service | |||
# Custom load balancer / proxy | |||
==== Architecture ==== | |||
<drawio filename="Setup:Installation_Guide_Docker-Achitecture" alt="Diagram of BlueSpice Docker Stack Architecture" /> | |||
'''Notes''' | |||
* Internal HTTP connections may use non-standard ports. Those are noted next to the respective services. | |||
** HTTP (in-secure) is only used for internal communication within the virtual network the stack is operated in. All connections to the client use TLS. | |||
* Proprietary ports (esp. for database connections) are noted next to the respective services. | |||
* There may be additional services and port in use, based on the setup. Some examples: | |||
** When using LDAP based authentication an LDAPS connection (port 636) is used from the <code>bluespice/wiki</code> containers to the LDAP-Server | |||
** When using Kerberos authentication, a connection (port 88) is used from the <code>bluespice/kerberos-proxy</code> containers to the Kerberos-Server | |||
** When using DeepL or OpenAI services, a HTTPS connection (port 443) is used from the <code>bluespice/wiki</code> containers to to the respective service | |||
** When using OpenIDConnect authentication, a HTTPS connection (port 443) is used from the <code>bluespice/wiki</code> "task" container to to the authentication provider | |||
** When using "Let's Encrypt" Certbot, a HTTPS connection (port 443) is used from the <code>acme-companion</code> container to the "Let's Encrypt" service | |||
=== Step 1: Get the stack === | |||
Get "docker-compose" files from https://bluespice.com/de/download/ | Get "docker-compose" files from https://bluespice.com/de/download/ | ||
wget <nowiki>https://bluespice.com/filebase/docker-deployment-script</nowiki> \ | wget <nowiki>https://bluespice.com/filebase/docker-deployment-script</nowiki> \ | ||
&& unzip docker-deployment-script \ | && unzip docker-deployment-script \ | ||
&& cd docker-deployment-script/compose | && cd docker-deployment-script/compose | ||
The directory contains the following files: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
!Filename | ! style="width:350px;" |Filename | ||
!Type | !Type | ||
! | !Mandatory | ||
!Comment | !Comment | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>bluespice-deploy</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>bluespice-deploy</code> | ||
|bash-script | |bash-script | ||
|false | |false | ||
|Wrapper for general start-up of needed | |Wrapper for general start-up of needed containers | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>bluespice-prepare</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>bluespice-prepare</code> | ||
|bash-script | |bash-script | ||
|false | |false | ||
|Prepare Folder and Permissions before first start also | |Prepare Folder and Permissions before first start also registers the service at the operating system | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>bluespice.service</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>bluespice.service</code> | ||
|service-script | |service-script | ||
|false | |false | ||
| | |Proper handling of the containers on reboot | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>docker-compose.main.yml</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>docker-compose.main.yml</code> | ||
|yml | |yml | ||
|true | |true | ||
|Main | |Main application services/ run by <code>bluespice-deploy</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml</code> | ||
|yml | |yml | ||
| | |false | ||
|Database and | |Database and search/ run by <code>bluespice-deploy</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>docker-compose.stateless-services.yml</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>docker-compose.stateless-services.yml</code> | ||
|yml | |yml | ||
| | |true | ||
|PDF-Renderer/Cache/Formula/Diagram-Service | |PDF-Renderer/Cache/Formula/Diagram-Service | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>docker-compose.proxy.yml</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>docker-compose.proxy.yml</code> | ||
|yml | |yml | ||
|false but recommended | |false, but recommended | ||
|Proxy Service | |Proxy Service | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml</code> | ||
|yml | |yml | ||
|false | |false | ||
|Additional | |Additional auto-renewal service for "Let's Encrypt" certificates | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<code>docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml</code> | | style="width:350px;" |<code>docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml</code> | ||
|yml | |yml | ||
|false | |false | ||
|Additional | |Additional proxy for Kerberos based authenication | ||
|} | |} | ||
For convenience, the <code>bluespice-deploy</code> script wraps the first four <code>yml</code> files by default. This includes the main wiki application and also required backend services, like a database, search and application cache. | |||
Additional services can be loaded by adding <code>-f <filename> </code>. | |||
Example: | |||
bluespice-deploy \ | |||
-f docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml \ | |||
up -d | |||
This will start the stack with "Let's Encrypt" certificates. For details, please refer to section [[#SSL certificates| SSL certificates]]. | |||
===Step 2: Set up environment variables=== | |||
Create <code>.env</code> file according to existing or state-to-be installation. | Create <code>.env</code> file according to existing or state-to-be installation. | ||
| Line 125: | Line 132: | ||
SMTP_PASS=... | SMTP_PASS=... | ||
SMTP_ID_HOST=... | SMTP_ID_HOST=... | ||
{{Textbox|boxtype=note|header=Different editions|text=The example shows <code>EDITION=pro</code>. Be aware that for <code>pro</code> and <code>farm</code> you need to be logged into <code>docker.bluspice.com</code>.|icon=yes}} | |||
Run <code>bluespice-prepare</code> script, helping you set up correct folder structure and permissions. Also installing a service for proper handling of the containers on reboots. | === Step 3: Prepare data directories=== | ||
Run <code>bluespice-prepare</code> script, helping you set up correct folder structure and permissions. Also installing a service for proper handling of the containers on reboots. Make sure to run this command with in a privileged user context (like <code>root</code>), as it will set permissions on the newly created directories. | |||
=== Step 4: Start the stack === | |||
{{Textbox | |||
|boxtype=important | |||
|header=Initial installation | |||
|text=When starting the stack the first time, the <code>wiki-task</code> container will automatically perform the installation. It may take a couple of minutes for the process to set up the database and complete. Once it is finished, the password for the default <code>Admin</code> user can be found in <code>$DATADIR/wiki/adminPasssword</code>. | |||
|icon=yes | |||
}} | |||
Use <code>bluespice-deploy up -d</code> to start the stack, once the <code>.env</code> file and the "data directories" are ready. Once all containers are shown as "ready" you can navigate to <code>$WIKI_PROTOCOL://$WIKI_HOST:$WIKI_PORT</code> (e.g. <code><nowiki>https://wiki.company.local</nowiki></code>) in your favorite web browser and start using the application. | |||
=== Additional options === | === Additional options === | ||
==== SSL certificates ==== | |||
For using Let's Encrypt | For using Let's Encrypt certificates just add <code>docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml</code> in your <code>bluespice-deploy</code> file. | ||
{{Textbox | {{Textbox | ||
| Line 140: | Line 158: | ||
}} | }} | ||
If | ====Operating system level service==== | ||
{{Textbox | |||
|boxtype=tip | |||
|header=Adding additional services | |||
|text=expand the <code>ExecStart</code> parameter in the <code>/etc/systemd/system/bluespice.service</code> | |||
Example: | |||
ExecStart=<WORKDIR>/bluespice-deploy -f docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml up -f -d --remove-orphans | |||
|icon=yes | |||
}} | |||
==== Custom wiki application configuration ==== | |||
After the initial installation, the <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/</code> contains two files that can be used to set custom application configuration as it may be found on [https://www.mediawiki.org mediawiki.org]: | |||
* <code>pre-init-settings.php</code> - Can be used to set config that can be picked up by the init process | |||
* <code>post-init-settings.php</code> - Can be used to manipulate configs that have been set by the init process | |||
==== Custom database and search ==== | |||
If you have a MySQL/MariaDB and an OpenSearch server running in your local network, you can remove <code>docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml</code> entirely from your <code>bluespice-deploy</code> file. Make sure to set the proper variables in the <code>.env</code> file. | |||
====Kerberos proxy==== | |||
For implicit authenticationusing Kerberos, an additional proxy must be used: <code>bluespice/kerberos-proxy</code> . The file <code>docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml</code> contains a common configuration. It can be used '''instead of''' the regular <code>docker-compose.proxy.yml</code> file inside <code>bluespice-deploy</code> . | |||
Make sure to have the files | |||
* <code>${DATADIR}/kerberos/krb5.conf</code> | |||
* <code>${DATADIR}/kerberos/kerberos.keytab</code> | |||
set up properly. | |||
The file <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/pre-init-settings.php</code> can then be used to set up [[mediawikiwiki:LDAP_hub|"Extension:Auth_remoteuser" and the LDAP stack extensions]]. | |||
====SAML authentication==== | |||
During the initial installation a certificate for message signing will automatically be created. It can be found in <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/certs/</code>. | |||
In order to configure a remote IdP, one must copy the IdP metadata XML to a file called <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/saml_idp_metadata.xml</code>. The SP metadata can then be obtained via <code><nowiki>https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/saml/sp/metadata.php/default-sp</nowiki></code>. It must be configured in the remote IdP. | |||
{{Textbox | |||
|boxtype=tip | |||
|header=Test authentication | |||
|text= You can test authentication directly within the SimpleSAMLphp application. To do so, navigate to <code><nowiki>https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/admin</nowiki></code> and log in with <code>admin</code> and the <code>INTERNAL_SIMPLESAMLPHP_ADMIN_PASS</code> found in <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/.wikienv</code> | |||
|icon=yes | |||
}} | |||
Next, the extensions "PluggableAuth" and "SimpleSAMLphp" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
wfLoadExtensions( [ | |||
'PluggableAuth', | |||
'SimpleSAMLphp' | |||
] ); | |||
</syntaxhighlight>[[File:Setup:SAML ConfigManager EN 01.png|thumb|300x300px]]to the <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php</code>. Run | |||
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick | |||
to complete the installation. | |||
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in [[Manual:Extension/BlueSpiceConfigManager|Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager]] under "Authentication". | |||
==== OpenID Connect authentication ==== | |||
The extensions "PluggableAuth" and "OpenIDConnect" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | |||
wfLoadExtensions( [ | |||
'PluggableAuth', | |||
'OpenIDConnect' | |||
] ); | |||
</syntaxhighlight>to the <code>${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php</code>. Run | |||
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick | |||
to complete the installation. | |||
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in [[Manual:Extension/BlueSpiceConfigManager|Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager]] under "Authentication". | |||
[[de:Setup:Installationsanleitung/Docker]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:47, 10 December 2024
- There are no "all-in-one" containers anymore. Neither for FREE, nor for PRO and FARM editions
- The "distributed-services" setup for PRO and FARM edition has completely been reworked
If you are upgrading from one of the above-mentioned setups, please refer to the migration guide
Overview
Since version 4.5, BlueSpice MediaWiki can be easily installed using a stack of Docker container images. Everything is build in a modular way to allow different types of setups.
The most common cases are
- "All-in-one" (with and without Let's Encrypt)
- Custom database and search service
- Custom load balancer / proxy
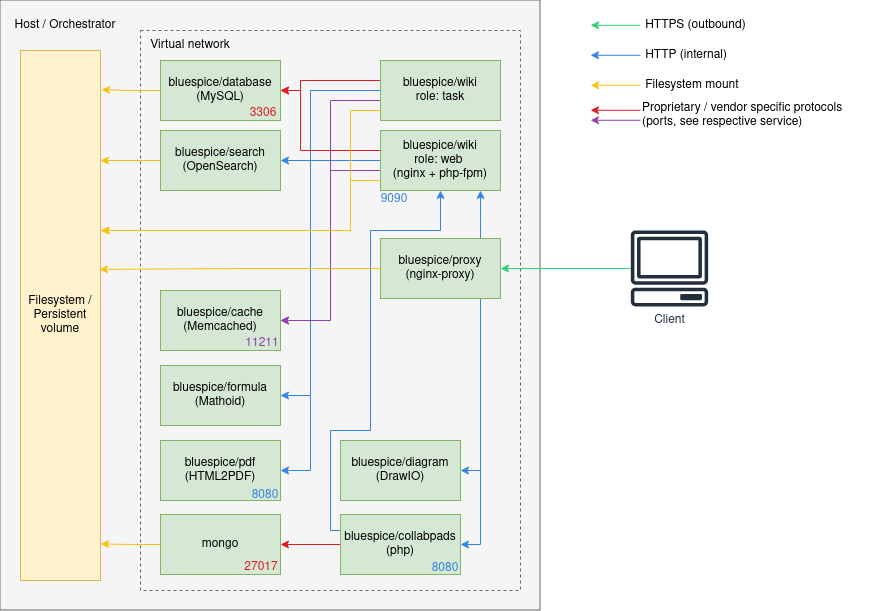
Architecture
Notes
- Internal HTTP connections may use non-standard ports. Those are noted next to the respective services.
- HTTP (in-secure) is only used for internal communication within the virtual network the stack is operated in. All connections to the client use TLS.
- Proprietary ports (esp. for database connections) are noted next to the respective services.
- There may be additional services and port in use, based on the setup. Some examples:
- When using LDAP based authentication an LDAPS connection (port 636) is used from the
bluespice/wikicontainers to the LDAP-Server - When using Kerberos authentication, a connection (port 88) is used from the
bluespice/kerberos-proxycontainers to the Kerberos-Server - When using DeepL or OpenAI services, a HTTPS connection (port 443) is used from the
bluespice/wikicontainers to to the respective service - When using OpenIDConnect authentication, a HTTPS connection (port 443) is used from the
bluespice/wiki"task" container to to the authentication provider - When using "Let's Encrypt" Certbot, a HTTPS connection (port 443) is used from the
acme-companioncontainer to the "Let's Encrypt" service
- When using LDAP based authentication an LDAPS connection (port 636) is used from the
Step 1: Get the stack
Get "docker-compose" files from https://bluespice.com/de/download/
wget https://bluespice.com/filebase/docker-deployment-script \
&& unzip docker-deployment-script \
&& cd docker-deployment-script/compose
The directory contains the following files:
| Filename | Type | Mandatory | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
bluespice-deploy
|
bash-script | false | Wrapper for general start-up of needed containers |
bluespice-prepare
|
bash-script | false | Prepare Folder and Permissions before first start also registers the service at the operating system |
bluespice.service
|
service-script | false | Proper handling of the containers on reboot |
docker-compose.main.yml
|
yml | true | Main application services/ run by bluespice-deploy
|
docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml
|
yml | false | Database and search/ run by bluespice-deploy
|
docker-compose.stateless-services.yml
|
yml | true | PDF-Renderer/Cache/Formula/Diagram-Service |
docker-compose.proxy.yml
|
yml | false, but recommended | Proxy Service |
docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml
|
yml | false | Additional auto-renewal service for "Let's Encrypt" certificates |
docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml
|
yml | false | Additional proxy for Kerberos based authenication |
For convenience, the bluespice-deploy script wraps the first four yml files by default. This includes the main wiki application and also required backend services, like a database, search and application cache.
Additional services can be loaded by adding -f <filename> .
Example:
bluespice-deploy \
-f docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml \
up -d
This will start the stack with "Let's Encrypt" certificates. For details, please refer to section SSL certificates.
Step 2: Set up environment variables
Create .env file according to existing or state-to-be installation.
Example:
DATADIR=/data/bluespice VERSION=4.5 EDITION=pro BACKUP_HOUR=04 WIKI_NAME=BlueSpice WIKI_LANG=en WIKI_PASSWORDSENDER=no-reply@wiki.company.local WIKI_EMERGENCYCONTACT=no-reply@wiki.company.local WIKI_HOST=wiki.company.local WIKI_PORT=443 WIKI_PROTOCOL=https DB_USER=bluespice DB_PASS=... DB_HOST=database DB_NAME=bluespice DB_PREFIX= SMTP_HOST=mail.company.local SMTP_PORT=25 SMTP_USER=... SMTP_PASS=... SMTP_ID_HOST=...
EDITION=pro. Be aware that for pro and farm you need to be logged into docker.bluspice.com.
Step 3: Prepare data directories
Run bluespice-prepare script, helping you set up correct folder structure and permissions. Also installing a service for proper handling of the containers on reboots. Make sure to run this command with in a privileged user context (like root), as it will set permissions on the newly created directories.
Step 4: Start the stack
wiki-task container will automatically perform the installation. It may take a couple of minutes for the process to set up the database and complete. Once it is finished, the password for the default Admin user can be found in $DATADIR/wiki/adminPasssword.
Use bluespice-deploy up -d to start the stack, once the .env file and the "data directories" are ready. Once all containers are shown as "ready" you can navigate to $WIKI_PROTOCOL://$WIKI_HOST:$WIKI_PORT (e.g. https://wiki.company.local) in your favorite web browser and start using the application.
Additional options
SSL certificates
For using Let's Encrypt certificates just add docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml in your bluespice-deploy file.
<bluespice-wiki.com>.crt and <bluespice-wiki.com>.key with the exact name of your Wikis URL in ${VOLUMES_DIR}/nginx/certs
Operating system level service
ExecStart parameter in the /etc/systemd/system/bluespice.service
Example:
ExecStart=<WORKDIR>/bluespice-deploy -f docker-compose.proxy-letsencrypt.yml up -f -d --remove-orphans
Custom wiki application configuration
After the initial installation, the ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/ contains two files that can be used to set custom application configuration as it may be found on mediawiki.org:
pre-init-settings.php- Can be used to set config that can be picked up by the init processpost-init-settings.php- Can be used to manipulate configs that have been set by the init process
Custom database and search
If you have a MySQL/MariaDB and an OpenSearch server running in your local network, you can remove docker-compose.persistent-data-services.yml entirely from your bluespice-deploy file. Make sure to set the proper variables in the .env file.
Kerberos proxy
For implicit authenticationusing Kerberos, an additional proxy must be used: bluespice/kerberos-proxy . The file docker-compose.kerberos-proxy.yml contains a common configuration. It can be used instead of the regular docker-compose.proxy.yml file inside bluespice-deploy .
Make sure to have the files
${DATADIR}/kerberos/krb5.conf${DATADIR}/kerberos/kerberos.keytab
set up properly.
The file ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/pre-init-settings.php can then be used to set up "Extension:Auth_remoteuser" and the LDAP stack extensions.
SAML authentication
During the initial installation a certificate for message signing will automatically be created. It can be found in ${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/certs/.
In order to configure a remote IdP, one must copy the IdP metadata XML to a file called ${DATADIR}/wiki/simplesamlphp/saml_idp_metadata.xml. The SP metadata can then be obtained via https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/saml/sp/metadata.php/default-sp. It must be configured in the remote IdP.
https://{{$WIKI_HOST}}/_sp/module.php/admin and log in with admin and the INTERNAL_SIMPLESAMLPHP_ADMIN_PASS found in ${DATADIR}/wiki/.wikienv
Next, the extensions "PluggableAuth" and "SimpleSAMLphp" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add
wfLoadExtensions( [
'PluggableAuth',
'SimpleSAMLphp'
] );
to the ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php. Run
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick
to complete the installation.
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager under "Authentication".
OpenID Connect authentication
The extensions "PluggableAuth" and "OpenIDConnect" must be enabled on the wiki. To do so, add
wfLoadExtensions( [
'PluggableAuth',
'OpenIDConnect'
] );
to the ${DATADIR}/wiki/bluespice/post-init-settings.php. Run
./bluespice-deploy exec wiki-task /app/bluespice/w/maintenance/update.php --quick
to complete the installation.
After that, the authentication plugin configuration can be applied in Special:BlueSpiceConfigManager under "Authentication".